Diabetes Melitus Epidemiologi Pdf
Global prevalence of diabetes estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030 sarah wild, mb bchir, phd 1 gojka roglic,md 2 anders green, md, phd, dr med sci 3 richard sicree, mbbs, mph 4 hilary king md dsc 2 objective— the goal of this study was to estimate the prevalence of diabetes and the number of people of all ages with diabetes for years 2000 and 2030.
Epidemiology Of Diabetes Mellitus An International
2. 1. 1 epidemiologi diabetes melitus (dm) prevalensi penderita dm di seluruh dunia sangat tinggi dan cenderung meningkat setiap tahun. jumlah penderita dm di seluruh dunia mencapai 422 juta penderita pada tahun 2014. jumlah penderita tersebut jauh meningkat dari tahun 1980 yang hanya 180 juta penderita. Be representative for the epidemiology of type 1 diabetes. especially when estimating the incidence of type 1 diabetes, the latency of onset until diag‐ nosis is important and influences the quality of estimated data. Classification of diabetes mellitus 5 introduction since 1965 the world health organization has periodically updated and published guidance on how to classify diabetes mellitus (hereafter referred to as “diabetes”) (1). this document provides an update on the guidance last published in 1999 (2).
Diabetes Who
Global report on diabetes who.
The Epidemiology Of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes epidemiology: guiding clinical and public health.
National Diabetes Statistics Report 2020 Estimates Of

Diabetes Epidemiology Guiding Clinical And Public Health
The epidemiology of diabetes mellitus: an international perspective is a long overdue, and welcome response to these population differences. epidemiological study has made a major contribution to our understanding of diabetes and its complications. The global prevalence (age-standardized) of diabetes has nearly doubled since 1980, rising from 4. 7% to 8. 5% diabetes melitus epidemiologi pdf in the adult population. this reflects an increase in associated risk factors such as being overweight or obese. over the past decade, diabetes prevalence has risen faster in lowand middle-income countries than in high-income countries. Pdf diabetes mellitus (dm) also known as simply diabetes, is a group of metabolic diseases in which there are high blood sugar levels over a prolonged find, read and cite all the research. 2. estimating the epidemiology of type 1 diabetes mellitus the epidemiology of type 1 diabetes can be estimated in different ways. in principle, there is the possibility of estimating epidemiologic data by self-report of the patients, longitudinal-or cross-sectional studies or different-sized registries.
The national diabetes statistics report pdf icon [pdf 768 kb] is a periodic publication of the centers for disease control and prevention (cdc) that provides updated statistics about diabetes in the united states for a scientific audience.. the report includes information on prevalence and incidence of diabetes, prediabetes, risk factors for complications, acute and long-term complications. Statistics about diabetes overall numbers. prevalence: in 2018, 34. 2 million americans, or 10. 5% of the population, had diabetes. nearly 1. 6 million americans have type 1 diabetes, including about 187,000 children and adolescents; undiagnosed: of the 34. 2 million adults with diabetes, 26. 8 million were diagnosed, and 7. 3 million were undiagnosed. The global prevalence (age-standardized) of diabetes has nearly doubled since 1980, rising from 4. 7% to 8. 5% in the adult population. this reflects an increase in associated risk factors such as being overweight or.
2017 national diabetes statistics report and is intended for a scientific audience. methods. new in 2020, this national diabetes statistics report features trends in prevalence and incidence. estimates over time. the estimates in this document (unless otherwise noted) were derived from various data systems of. Diabetic retinopathy is an important cause of blindness, and occurs as a result of long-term accumulated damage to the small blood vessels in the retina. 2. 6% of global blindness can be attributed to diabetes (2). diabetes is among the leading causes of kidney failure (3).
Diabetes rates in the united states, like across north america and around the world, have been increasing substantially. according to the 2014 statistics report done by the cdc it was found that, “diabetes mellitus affects an estimated 29. 1 million people in the united diabetes melitus epidemiologi pdf states and is the 7th leading cause of death. Prevalence of diabetes mellitus (%) indicator code: e040606. t this indicator shares the definition with the parent indicator \"number of all cases of diabetes mellitus at year's end\". cumulative number of patients with diabetes (icd-9: 250; icd-10: e10-e14) at the end of the calendar year. The epidemic nature of diabetes mellitus in different regions is reviewed. the middle east and north africa region has the highest prevalence of diabetes in adults (10. 9%) whereas, the western pacific region has the highest number of adults diagnosed with diabetes and has countries with the highest prevalence of diabetes (37. 5%). The global epidemic of type 2 diabetes mellitus (t2dm) and its complications is a major threat to public health. this review provides an updated view of the global epidemiology of t2dm and the.
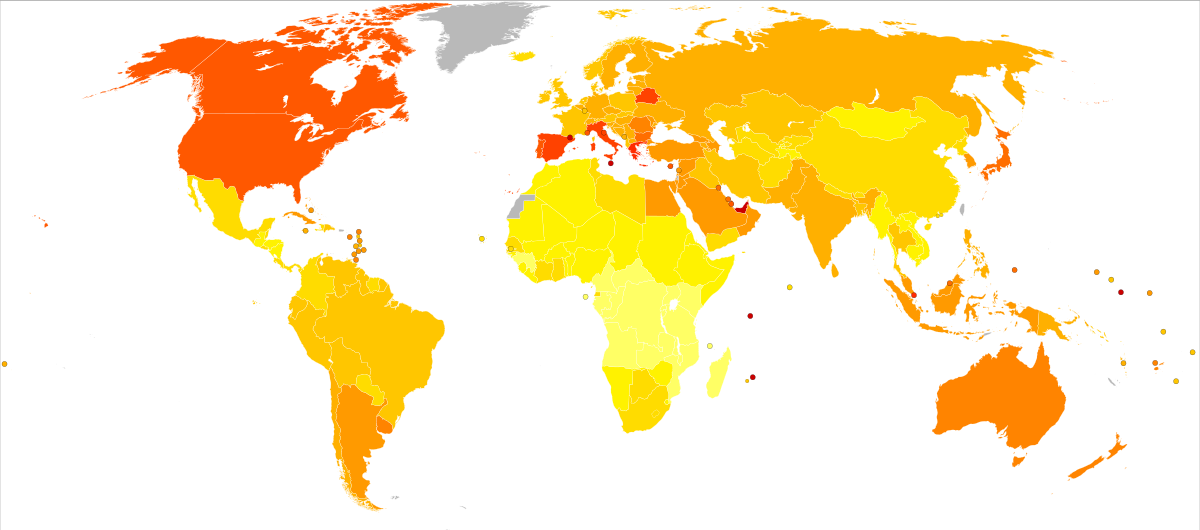
National diabetes statistics report, 2020. 1. introduction. the national diabetes statistics report, a periodic publication of the centers for disease control and. prevention (cdc), provides information on the prevalence and incidence of diabetes and prediabetes, risk factors for complications, acute and long-term complications, deaths, and costs. Mellitus prevalence is 2,9%. factors that have significant relationship with diabetes are age, family history, protein and fat consumption, vegetable and fruit. Diabetesmellitus (dm) is one of the most common chronic diseases affecting the general population, with an increasing prevalence worldwide (1). the end-organ damage, including retinopathy. The global prevalence of diabetes* among adults over 18 years of age rose from 4. 7% in 1980 to 8. 5% in 2014 (1). between 2000 and 2016, there was a 5% increase in premature mortality from diabetes. diabetes prevalence has been rising more rapidly in lowand middle-income countries than in high-income countries.

Diabetes mellitus (dm), also known as simply diabetes, is a group of metabolic diseases in which there are high blood sugar levels over a prolonged period. Diabetesmellitus (dm), commonly known as diabetes, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level over a prolonged period of diabetes melitus epidemiologi pdf time. symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst, and increased appetite. if left untreated, diabetes can cause many complications. acute complications can include diabetic ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state, or. Epidemiology provides a scientific basis for clinical and public health practice. indeed, epidemiology can be used to guide how we define, diagnose, and screen for diabetes, to describe the present and future burden of diabetes, and to highlight opportunities for intervention. diabetes is a group of disorders characterized by high glucose levels that cause unique eye, kidney, and nerve. The incidence of type 1 diabetes in children varies nearly 400-fold between countries with age-adjusted incidence rates ranging from 0. 1 per 100,000 per year in parts of venezuela and china to 37. 8 in sardinia and 40. 9 per 100,000/year in finland. 1 the high rate observed in sardinia is notably discordant with the incidence in italy as a whole.. incidence also varies within several other.
Introduction. diabetes mellitus (dm) is one of the largest global health emergencies of the 21st century and the seventh leading cause of death in the usa in 2010 1. dm is also a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease (cvd), which is the most common cause of death among adults with dm 2. besides the well-recognized microvascular complications of dm, such as nephropathy and retinopathy. Diabetes melitus tidak dapat disembuhkan tetapi kadar gula darah dapat dikendalikan melalui diet, olah raga, dan obat-obatan. untuk dapat mencegah terjadinya komplikasi kronis, diperlukan pengendalian dm yang baik (perkeni, 2011). 2. 1. 2 klasifikasi diabetes melitus klasifikasi etiologi diabetes mellitus menurut american diabetes. A. diabetes mellitus (d m) 1. definisi dm diabetes melitus adalah suatu keadaan didapatkan peningkatan kadar gula darah yang kronik sebagai akibat dari gangguan pada metabolisme karbohidrat, lemak, dan protein karena kekurangan hormone insulin. masalah utama pada penderita dm ialah terjadinya komplikasi, khususnya. Introduction type 2 diabetes mellitus is a major source of morbidity and mortality in south africa, spurred by increased urbanisation and unhealthy lifestyle factors. local epidemiological data are required to inform health planning and policy. the purpose of this systematic review is to identify, collate and synthesise all studies reporting the prevalence of diabetes in south africa.
Comments
Post a Comment