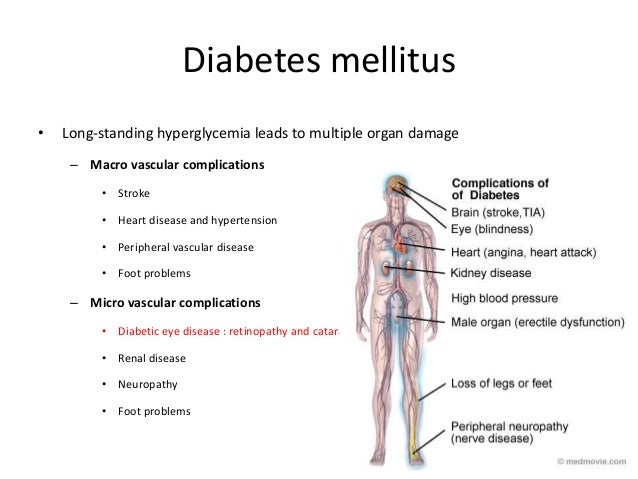
Diabetes Complications Microvascular
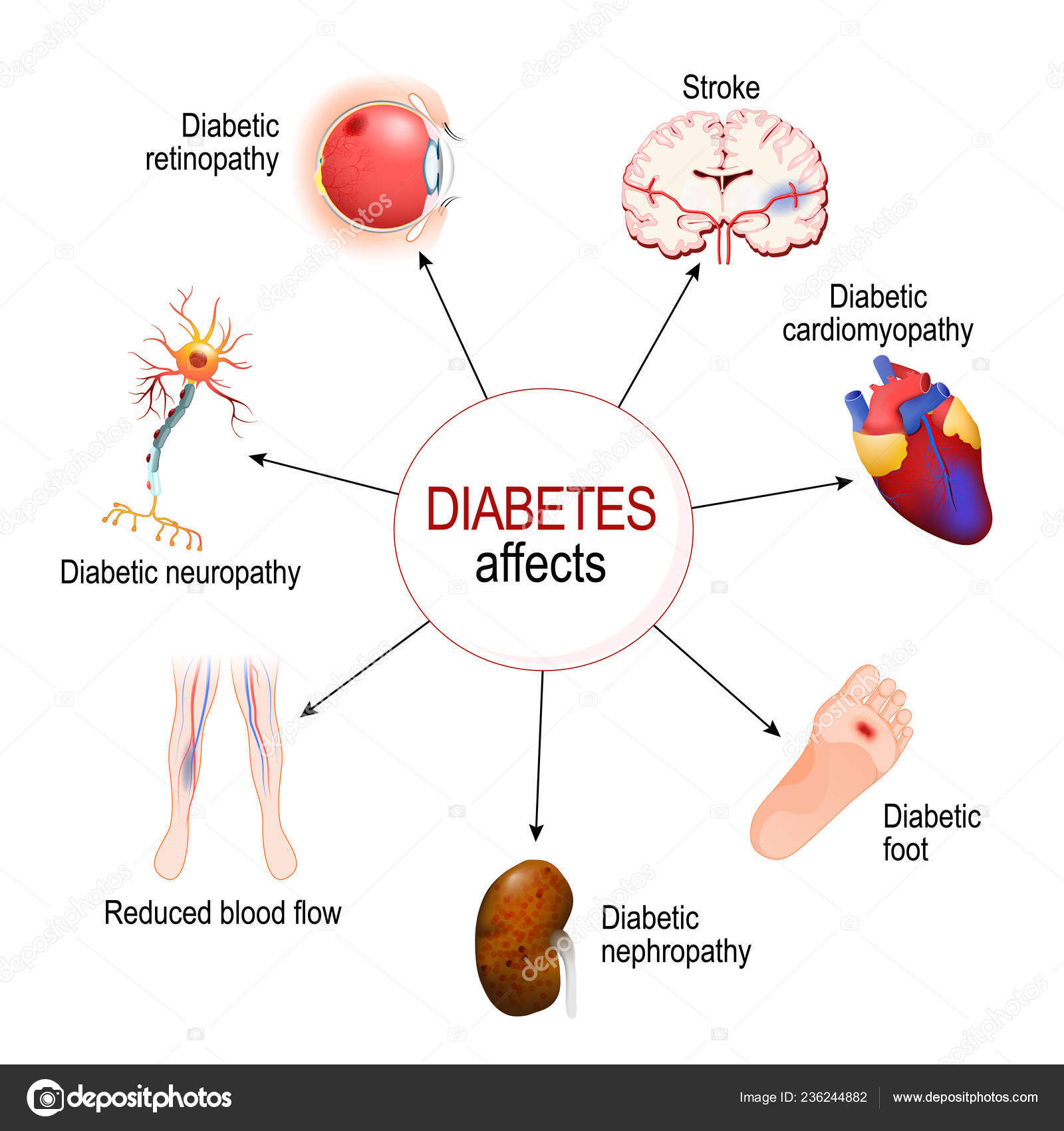
Diabetic retinopathy. diabetic retinopathy may be the most common microvascular complication of diabetes. it is responsible for ~ 10,000 new cases of blindness every year in the united states alone. 1 the risk of developing diabetic retinopathy or other microvascular complications of diabetes depends on both the duration and the severity of hyperglycemia. Complications of diabetes mellitus include problems that develop rapidly (acute) diabetes complications microvascular or over time (chronic) and may affect many organ systems. the complications of diabetes can dramatically impair quality of life and cause long-lasting disability. overall, complications are far less common and less severe in people with well-controlled blood sugar levels. Describes peripheral neuropathy, charcot foot, microvascular disease, and treatment. includes a case study with photos.
Relationship Between Hba1c And Risk Of Micromacrovascular
Diabetes is the leading cause of new vision loss among adults ages 20 to 74 in the u. s. it can lead to eye problems, some of which can cause blindness if not treated: glaucoma. Aims. much of the diabetes burden is caused by its complications. this cross-sectional study aimed to determine the prevalence and risk factors for diabetic microvascular complications (retinopathy, nephropathy, and neuropathy) in a high-risk population. methods. we collected information via a structured questionnaire and directly from the patient’s record on 1034 adult type 2 diabetic. The major microvascular complications are diabetic retinopathy, nephropathy, and neuropathy. the diabetic foot ulcer shown is the result of longstanding peripheral neuropathy. diabetic retinopathy is progressive damage to the retina from longstanding diabetes mellitus that, if untreated, will lead to progressive vision loss and blindness. consonant glycemic command leads to fewer long-term diabetes-related complications some natural ocular findings are reversible, such as
Complications of diabetes: microvascular.
Who About Diabetes
More diabetes complications microvascular images. blood pressure control and risk of macrovascular and microvascular complications in type 2 diabetes: ukpds 38 bmj 1998;317:703-713 157 and captopril in reducing risk of macrovascular and microvascular complications in type 2 diabetes:ukpds 39 bmj 1998;317:713-720 161 In light of the above strong evidence linking diabetes and cvd and to control and prevent the microvascular complications of diabetes, the ada has issued practice recommendations regarding the prevention and management of diabetes complications. blood pressure should be measured routinely. goal blood pressure is < 130/80 mmhg.
Macrovascular Complications In Patients With Diabetes And
Microvascularcomplications of diabetes prevention and treatment of eye, kidney and nerve disease www. diabetesed. net beverly dyck thomassian, rn, mph, bc‐adm, cde president, diabetes education services diabetes –microvascular complications microvascular complications diabetic eye disease, nephropathy,. Diabetes is a leading cause of microvascular complications such as nephropathy and retinopathy. it is also associated with an accelerating atherosclerosis, and type 2 diabetes mellitus (t2dm) is usually not detected until late in the course of cardiovascular disease (cvd). Diabetescomplications are divided into microvascular (due to damage to small blood vessels) and macrovascular (due to damage to larger blood vessels). microvascular complications include damage to eyes (retinopathy) leading to blindness, to kidneys (nephropathy) leading to renal failure and to.
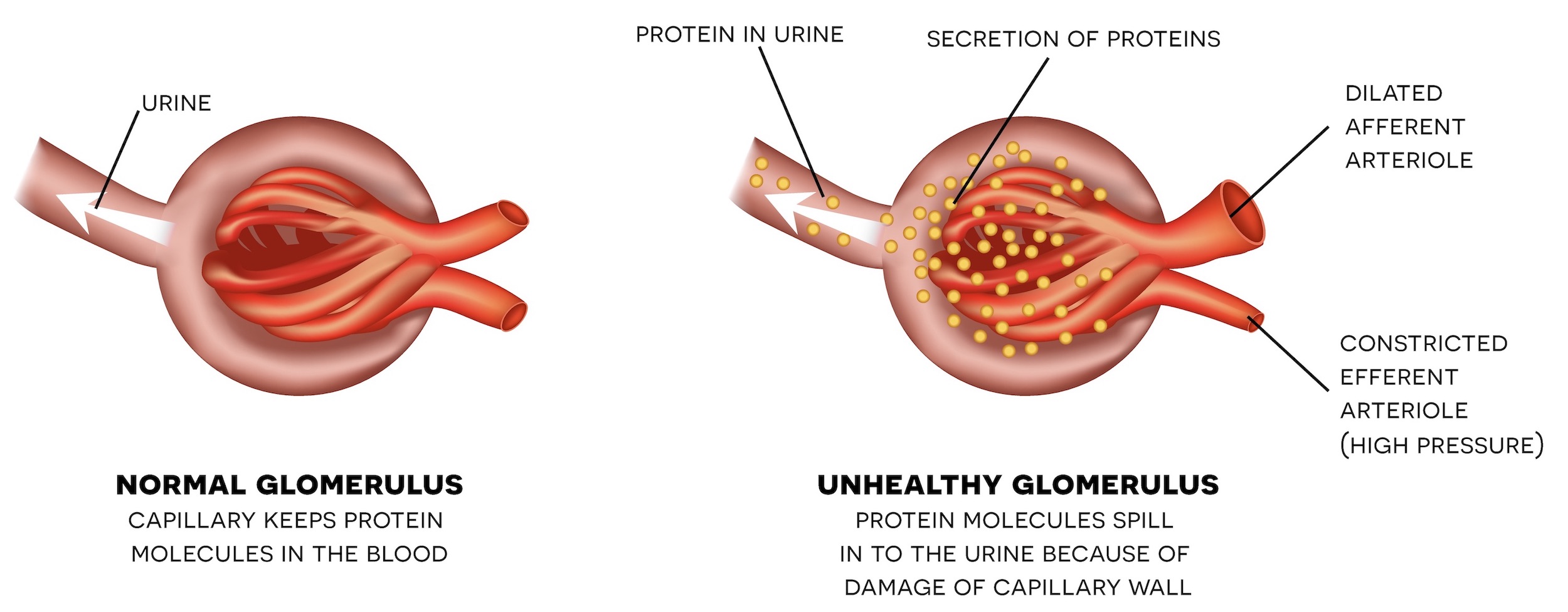
Relationship between hba1c and risk of micro/macrovascular complications and healthcare costs among type 2 diabetes poor glycemic control (>7. poor glycemic control (>7. 0%) in patients with type 2 diabetes (t2d) may increase risk of complications, leading to higher healthcare costs. Microvascularcomplications and foot care: standards of medical care in diabetes−2020 american diabetes association diabetes care 2020 jan; 43 (supplement 1): s135 s151. Microvascularcomplications damage to small blood vessels is called microangiopathy or microvascular disease. in microvascular disease, persistent hyperglycemia contributes to a thickening of the basement membrane in small blood vessels, which is thought to limit the passage of nutrients and oxygen to the tissues that these blood vessels supply.
Microvascular and macrovascular complications of diabetes.

Mean diabetes-related health expenditure per person, usd; mean diabetes-related health expenditure per person, id; demographics. total adult population (20-79 y), in 1,000s; population of children (0-14 y), in 1,000s; population of children and adolescents (0-19 y), in 1,000s; complications of diabetes. microvascular; macrovascular. Microvascular complications of diabetes diabetic retinopathy diabetic retinopathy may be the most common microvascular complica-tion of diabetes. it is responsible for ~ 10,000 new cases of blindness every year in the united states alone. 1 the risk of developing diabetic retinopathy or other microvascular complications of diabetes diabetes complications microvascular depends.
Microvascular complications and foot care: standards of medical care in diabetes−2020 american diabetes association diabetes care 2020 jan; 43 (supplement 1): s135 s151. Microvascular complications damage to small blood vessels is called microangiopathy or microvascular disease. in microvascular disease, persistent hyperglycemia contributes to a thickening diabetes complications microvascular of the basement membrane in small blood vessels, which is thought to limit the passage of nutrients and oxygen to the tissues that these blood vessels supply.
Macrovascular diabetes complications. macrovascular complications are more commonly seen in diabetics with type 2 form than patients with type 1 diabetes. patients with type 2 diabetes normally undergo other cardiovascular risks, owing to obesity, hypertension and extra lipid or fat accumulation. macrovascular diseases are enhanced by smoking. Background: type 2 diabetes mellitus (t2dm) has emerged as a pandemic. it has different complications, both microvascular and macrovascular. objective: the purpose of this review is to summarize the different types of macrovascular complications associated with t2dm. Diabetes mellitus is expensive, but most of the costs are attributed to complications and hospital care. this article will review the recommendations from the ada 2017 standards of care for microvascular complications and relevant position statements, and will highlight preventive screening and clinical pearls for the primary care diabetes complications microvascular physician treating patients with diabetes. Diabetes complications are divided into microvascular (due to damage to small blood vessels) and macrovascular (due to damage to larger blood vessels). microvascular complications include damage to eyes (retinopathy) leading to blindness, to kidneys (nephropathy) leading to renal failure and to.
In 1975, the commission issued the long-range plan to combat diabetes, which included the recommendation for the national institutes of health (nih) to “initiate and support a 5-year clinical study to assess the effects of treatment of juvenile-onset diabetes on the development of microvascular and macrovascular complications. ”.
Comments
Post a Comment